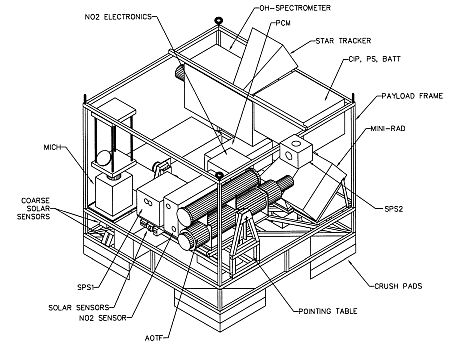
Purpose of the flight and payload description
MANTRA is a balloon mission to investigate changes in the concentrations of ozone and other compounds in the stratosphere.
The balloon carried a payload of six instruments to measure atmospheric composition and to investigate possible causes for the lack of agreement between theory and observations from the past.
Of the six instruments, three of them were flown on balloons in the 1970s and early 1980s:
- NO2 spectrophotometer
- HNO3 radiometer,
- OH spectrometer,
and three of them employed newer technology:
- photodiode array spectrometer
- acousto-optic tunable filter spectrometer
- Fourier transform interferometer.
Details of the balloon flight
Balloon launched on: 8/24/1998 at 3:25 CST
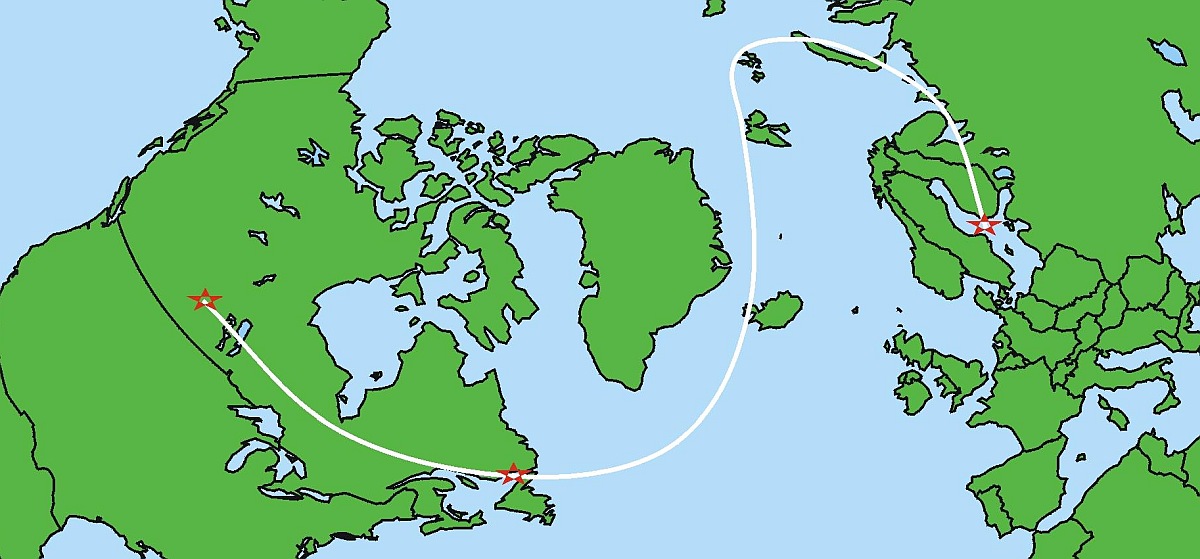
Launch site: Scientific Instrumentation Ltd Balloon Launch Facility, Vanscoy, Saskatchewan, Canada
Balloon launched by: Scientific Instrument Limited
Balloon manufacturer/size/composition: Zero Pressure Balloon 328.500 m3
End of flight (L for landing time, W for last contact, otherwise termination time): 9/2/1998
Balloon flight duration (F: time at float only, otherwise total flight time in d:days / h:hours or m:minutes - ): 9 d
Landing site: Near Mariehamn on the Aland Islands, located at Baltic Sea, Finland
Campaign: MANTRA
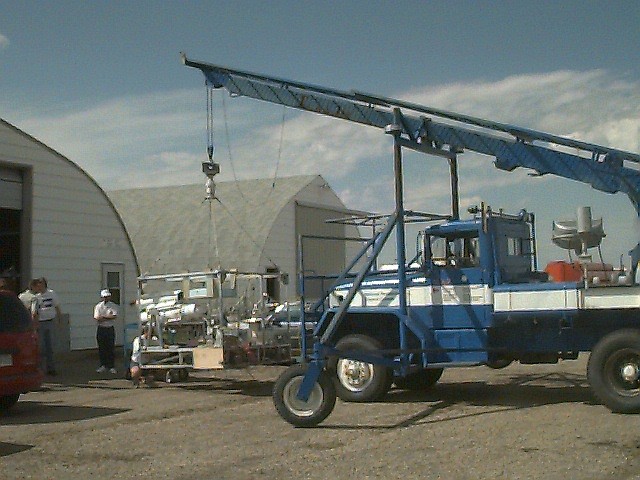
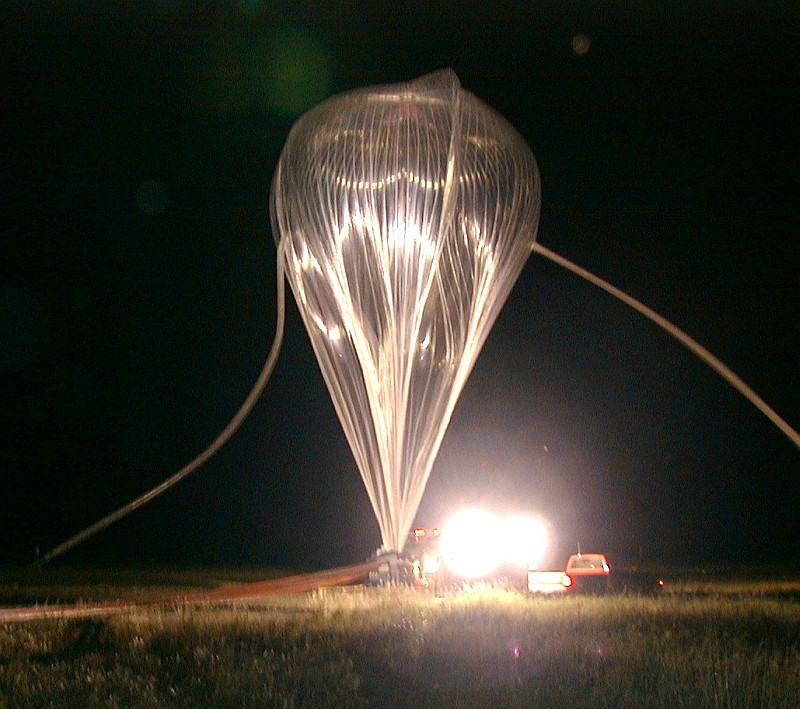
Balloon was launched from Vanscoy, at 3:25 am local time, by dynamic method using a launch vehicle.
The balloon reached float altitude without problems and spent the rest of the day, making the planned observations.
After successfully completing its mission, with the data sent by telemetry back to the ground base, the cutdown command was sent but nothing happened. All the separation gear failed
and the balloon journeyed across Canada, descending down into the trans-Atlantic air routes near Anticosti Island in the Gulf of St. Lawrence.
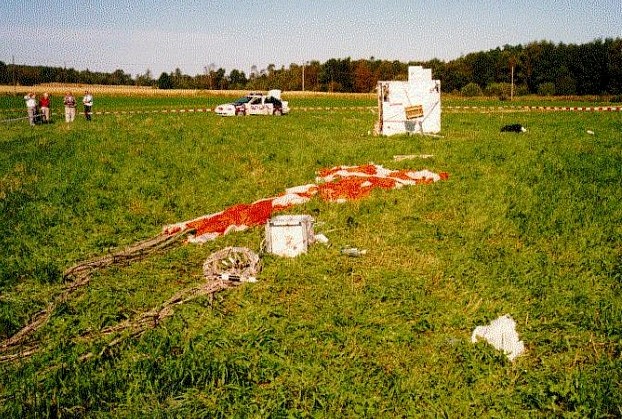
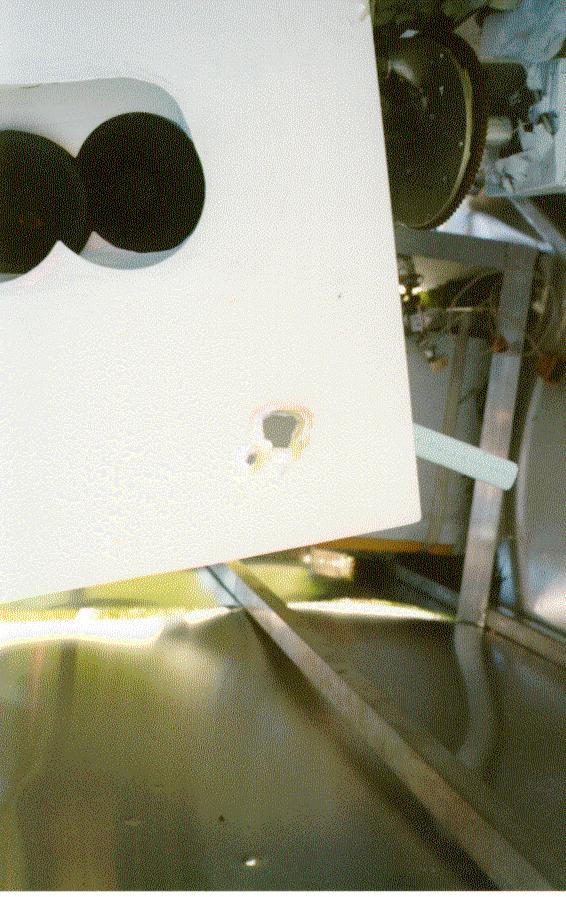
That was when worried air traffic controllers called the Canadian military in. CF-18 jet pilots fired on it more than 1,000 bullets and survived. The balloon continued on travelling over Iceland where it was shadowed by U.S. and British military aircraft, then past Spitsbergen, Norway, through Russian airspace and over Finland, when finally landed near Mariehamn on the Aland Islands, on September 2, nine days after its journey began.
The payload was recovered with the assistance of the Finnish Meteorological Institute.
External references
- MANTRA program University of Toronto
- Balloon-borne radiometer measurement of Northern Hemisphere mid-latitude stratospheric HNO3 profiles spanning 12 years Atmos. Chem. Phys., 7, 6075-6084, 2007
- MANTRA - A Balloon Mission to Study the Odd-Nitrogen Budget of the Stratosphere Atmosphere-Ocean, 43:4, 283 (2005)
- Runaway Canadian Science Balloon: MANTRA 1998 Dan Weaver website
- Summertime stratospheric processes at northern mid-latitudes: comparisons between MANTRA balloon measurements and the Canadian Middle Atmosphere Model Atmos. Chem. Phys., 8, 2057-2071, 2008
If you consider this website interesting or useful, you can help me to keep it up and running with a small donation to cover the operational costs. Just the equivalent of the price of a cup of coffee helps a lot.