Purpose of the flight and payload description
The objective of the flight was to collect stratospheric air samples for greenhouse gas measurements.
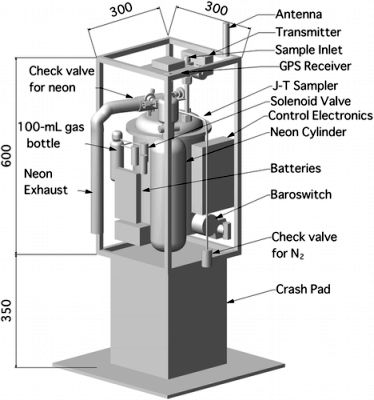
The payload can be seen in the scheme at left. It was a compact cryogenic air sampler of relativelly new design which uses a cooling device called the JouleThomson (JT) minicooler. The JT minicooler can produce liquefied neon within 5 seconds from high pressure neon gas precooled by liquid nitrogen. The sampler employs liquid neon as a refrigerant to solidify or liquefy sampled atmospheric constituents.
The sampler is capable of collecting about 3 and more than 7 L STP of air at 25 and 120 hPa, respectively, which corresponds to about 25 and 15 km above ground within 240 seconds, respectively.
The balloon-borne sampling system, which was developed specially for Antarctic experiments, consists of the compact sampler, a 2-L high pressure neon gas cylinder, pneumatic and solenoid valves, a controller with a GPS receiver, a telemetry transmitter, and batteries.
The size of the sampling system is 300 mm width × 300 mm depth × 950 mm height and it weighs about 22 kg (including liquid nitrogen), allowing the use of relativelly small balloons (2000m3 to 9000 m3).
Details of the balloon flight
Balloon launched on: 1/10/2013 at
Launch site: Syowa Station, Antarctica
Balloon launched by: National Institute of Polar Research (NIPR) / Institute of Space and Astronautical Science (ISAS)
Balloon manufacturer/size/composition: Zero Pressure Balloon 9.000 m3
End of flight (L for landing time, W for last contact, otherwise termination time): 12/31/2012
External references
- Trace Gas Research Group homepage Tohoku University website
- No Link Personal communication of Dr. Tetsuya Yoshida of ISAS / JAXA with StratoCat
If you consider this website interesting or useful, you can help me to keep it up and running with a small donation to cover the operational costs. Just the equivalent of the price of a cup of coffee helps a lot.