Purpose of the flight and payload description
The Japanese American Collaborative Emulsion Experiment (JACEE) was a scientific effort carried out to measure the composition and spectra of primary cosmic rays at the top of the atmosphere, using emulsion chambers transported by stratospheric balloons. JACEE's first flight was conducted in 1979, and flights continued through 1996, totaling 14 flights and 13 successful missions. The collaboration leveraged Japanese expertise in photographic materials and microscopy, American expertise in ballooning and data analysis, and Polish resources in scanning and measurement of emulsions.
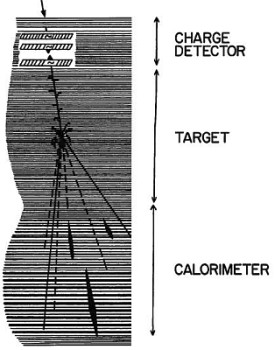
Each payload could contain one, three, or four chambers, each chamber with an area about 2000 cm2, 12~25 cm thick, and weighing ~120 kg. Figure at left shows a schematic diagram of the vertical configuration of one chamber. It was comprised of four sections, identifiable according to their function in the experiment. These are, from the top, the charge detector, the target, the spacer, and the calorimeter. All sections were multilayered stacks of track-sensitive materials (emulsions, x-ray films, CR-39, Lexan) alternated with absorbers (acrylic, lead). There were approximately 300 layers of emulsion in the chamber. This configuration was more or less the same for all the flights. However, many flights not included the spacer section, and in some cases were added other elements like Cerenkov detectors or plastic scintillators.
The charge detector employed thick (200 - 400 micron) emulsions, which permited accurate determination of the charge of each primary particle via measurements of the grain density, gap distribution, and/or delta ray distribution. The target section was comprised basically of thin (50 ~ 75 micron) emulsion plates alternated with acrylic sheets. The substantial mass of low-Z material maximized the interaction probability, while the emulsion optimized the observation of charged tracks from an interaction vertex. In order to identify nuclear fragments, charge identification layers composed of thick emulsions and etchable plastics were inserted at regular intervals throughout the target.
The spacer section consisted of honeycomb paper with a few thin emulsions positioned at regular intervals that facilitated the tracing of tracks through it. Finally, the calorimeter was the energy measuring portion of the apparatus. It consisted of 1.0 and 2.5 mm thick lead sheets alternating with thin emulsion plates and x-ray films. Gamma rays emanating from a vertex in the target initiated electro-magnetic cascades in the calorimeter. The cascades produced dark spots in the x-ray films, the observation of which provided the trigger for an event. The events were traced back from the calorimeter, through the spacer, to the vertex in the target by observing associated tracks in the emulsions.
All flights made in Antarctica for JACEE after 1992 used the same gondola design: a simple, lightweight and very rugged framework that provided protection for the emulsion chamber modules in case of an awkward landing or parachute drag, wich also was easy to dissasemble on the landing spot or to be replaced in short notice at a low cost. The payload included an onboard data logging computer which was an adaptation of electronics originally designed for other project to record pressure altitude and module temperatures, as well as to control a shifter mechanism which moved upper emulsion layers out of registration when the gondola altitude was below 6 mbar. The JACEE data logger was interfaced to the NSBF SIP (Support Instrument Package) allowing status monitoring and data downloading during flight.
Details of the balloon flight
Balloon launched on: 1/2/1994 at 00:44 utc
Launch site: Williams Field, McMurdo Station, Antarctica
Balloon launched by: National Scientific Balloon Facility (NSBF)
Balloon manufacturer/size/composition: Zero Pressure Balloon N29EX-8/8/8T-28.40-01
Balloon serial number: R28.40-2X-105
Flight identification number: 375NT
End of flight (L for landing time, W for last contact, otherwise termination time): 1/10/1994 at 22:08 utc
Balloon flight duration (F: time at float only, otherwise total flight time in d:days / h:hours or m:minutes - ): ~ 9 d
Landing site: 443 miles ESE of McMurdo, Antarctica
Payload weight: 3015 lbs
Overall weight: 4537 lbs
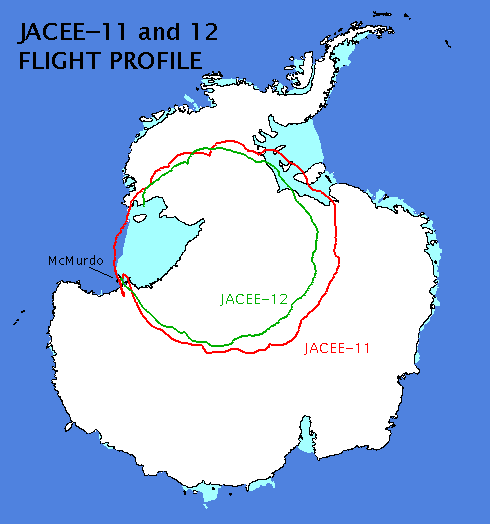
The balloon was launched by dynamic method on January 2, 1994 at 0:44 utc. After a nominal climb to float altitude it started a counter clock-wise path over Antarctica which is reproduced in the image at right (JACEE-12 path in green). The mission, after a complete turn around the south pole was terminated on January 10 at 22:08 utc. The payload landed in a spot located 443 nautic miles ESE of McMurdo Station.
The summer 1993/1994 NASA balloon launch season in Antarctica was the first time that two JACEE payloads where flown. This was the second launch of the campaign and was a complete success logging near 210 hours of exposure.
External references
- JACEE experiment website Institute of Nuclear Physics PAN, Poland (via Archive.Org)
- JACEE experiment website University of Washington Particle Astrophysics Group (via Archive.Org)
- Antarctic Balloon Flights for JACEE 24th International Cosmic Ray Conference, Vol. 3, Pag. 615
- Cosmic Ray Astrophysics from Balloons in Antarctica Astrophysics From Antarctica; ASP Conference Series; Vol. 141; 1998, p.26
- Cosmic-Ray Proton and Helium Spectra: Results from the JACEE Experiment Astrophysical Journal Vol. 502 Pag 278, 1998
- Elemental abundance of high energy cosmic rays Nuclear Physics B - Proceedings Supplements - Vol. 60, Issue 3, p. 83
- Energy spectra and elemental composition of nuclei above 100-TeV from a series of JACEE balloon flights UWSEA PUB 94-07, Proc. 24th ICRC 2:707
- NASA Balloon Flights (19891998) in NASA Historical Data Book, Vol. VII: NASA Launch Systems, Space Transportation, Human Spaceflight, and Space Science, 1989-1998
If you consider this website interesting or useful, you can help me to keep it up and running with a small donation to cover the operational costs. Just the equivalent of the price of a cup of coffee helps a lot.