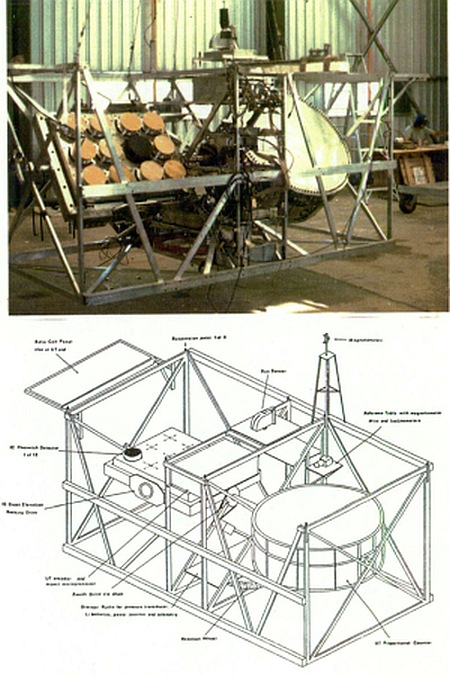
Purpose of the flight and payload description
In this flight were transported two instruments: a large area phoswich array provided by the Imperial College Group and a large area proportional counter developed by the University of Tasmania. The goal of the flight was to investigate hard cosmic X-ray sources from the southern hemisphere.
The large area phoswich array consisted of 12 identical modules totalling 1600 cm2. Each module had a primary 2 mm thick NaI crystal backed by a 14 mm thick CsI crystal, and a 2° FWHM field of view produced by a tantalum honeycomb collimator; passive shielding was used to block background radiation through the sides. Photons were detected in 31 energy channels over the range 16-200 keV.
The other instrument was a multilayer, multianode proportional counter with an area of 5200 cm2 and 21 cm active depth, filled with Xenon at 1 atmosphere. Its 10-100 keV range was spanned by 20 energy channels. A thin alloy honeycomb collimator defined the 2° FWHM field of view, while the rear and sides were screened by a graded shield. Background due to charged particles was also removed by active screening.
Details of the balloon flight
Balloon launched on: 3/25/1983 at 03:42
Launch site: Balloon Launch Sector, Cachoeira Paulista, Brazil
Balloon launched by: Instituto Nacional de Pesquisas Espaciais (INPE)
Balloon manufacturer/size/composition: Zero Pressure Balloon
End of flight (L for landing time, W for last contact, otherwise termination time): 3/25/1983 at ~ 13:40
Balloon flight duration (F: time at float only, otherwise total flight time in d:days / h:hours or m:minutes - ): 10 h
Landing site: In Fazenda Sao Jose, Itaí (SP), Brazil
The balloon was launched from the INPE base in Cachoeira Paulista, Brazil at 6:40 UTC on 26th March 1983. It remained at a float attitude, corresponding to a vertical atmospheric absorption of 4.1 g/cm2 between 11:20 utc and 17:00 utc. The flight ended with a balloon failure at float altitude. Apparently the balloon burst and became entangled with the parachute, and as a result the payload was completely destroyed upon impact.
During the flight were observed four X-Ray sources: Sco X-1, SS433, MR2251-178 and SMC X-1
External references
- A infraestrutura do INPE para lancar balao cientifico Elisete Rinke dos Santos, editorial Transtec, 1993
- Balloon altitude studies of southern hemisphere hard X-ray sources by the Imperial College-University of Tasmania-INPE collaboration Advances in Space Research, Volume 3, Issue 10-12, p. 43
- Hard X-ray observations of Sco X-1 and GX 1+4 PhD thesis by Stefan W. Dieters, University of Tasmania, 1990
If you consider this website interesting or useful, you can help me to keep it up and running with a small donation to cover the operational costs. Just the equivalent of the price of a cup of coffee helps a lot.