Purpose of the flight and payload description
The detector system was formed by a telescope composed by two Geiger-Muller counters. One of the counters had a thin cover of Aluminium, whereas the second had a internal cover of Bismute. The counting rates of each counter and its double coincidence were transmitted by telemetry.
The solar event of August 7, 1972 was the first case in which secondary X rays resulting from solar X-ray emission have been observed at large atmospheric depths, the duration of the effects being some tens of minutes.
Aditionally the balloon carried on board a Maurer photographic camera loaded with infrared film. During the flight were obtained the first pictures in colour taken from above 20 km of altitude in Argentina.
It was also the first balloon launched entirely by Argentine staff.
Details of the balloon flight
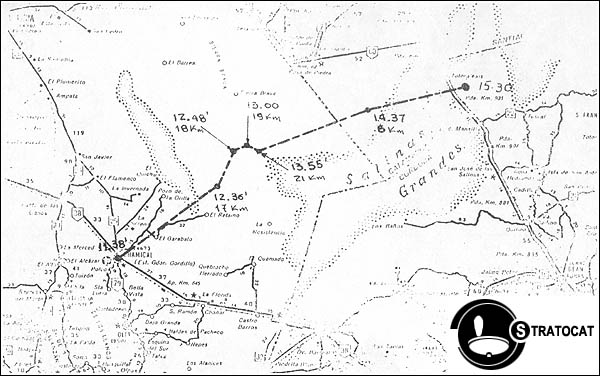
Balloon launched on: 8/7/1972 at 11:38 local
Launch site: Centre for Experimentation and Launch of Self-Propelled Rockets, Chamical, Argentine
Balloon launched by: Instituto de Astronomía y Física del Espacio
Balloon manufacturer/size/composition: Zero Pressure Balloon 500.000 ft3
End of flight (L for landing time, W for last contact, otherwise termination time): 8/7/1972 at ~ 15:30 local
Balloon flight duration (F: time at float only, otherwise total flight time in d:days / h:hours or m:minutes - ): ~ 4 h
Landing site: 12 km E of the town of Totoralejos, in the zone of Salinas Grandes, Cordoba province
Overall weight: 87 kgs
Predetermined cut down by mechanical timer
External references
- An X-Ray Observation in the Atmosphere During the August 7, 1972 Solar Flare Astrophysics and Space Science, Volume 226, Issue 1, pp.19-26
- Primera fotografia color desde mas de 20 km obtenida en el pais Raul P. Flores, published by CNIE - December 1972 (StratoCat's private collection)
- Una observación de rayos X en la atmósfera durante la erupción solar del 7 de agosto de 1972 Geoacta; vol. 8, no. 1, 1976, Pag. 165
If you consider this website interesting or useful, you can help me to keep it up and running with a small donation to cover the operational costs. Just the equivalent of the price of a cup of coffee helps a lot.

