Purpose of the flight and payload description
This flight was part of a program developed at the Department of Physics, Imperial College of Science and Technology in London, with support from the Cosmic Rays and Space Physics Group to measure low-energy primary cosmic ray electrons in the 25-600 MeV range. The experiments involved balloon flights carrying detectors launched from two locations: Kiruna Geophysical Observatory in Northern Sweden and RAF Cardington in England, between 1964 and 1966.
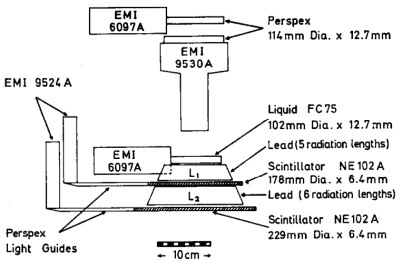
In the scheme at left we can see the so called "B" detector aimed to determine the differential energy spectrum of the primary cosmic ray electrons at the top of the atmosphere.
The B detector employed a Cerenkov telescope with a threshold of ß = 0.78. The device contained Perspex material measuring 102mm in diameter and 12.7mm in thickness and incorporated a lead-scintillator sandwich detector for energy measurement, with the lead absorber split into two sections: an upper block of five radiation lengths and a lower block of six radiation lengths. The scintillator components used NE 102A material, each measuring 229mm in diameter and 6.4mm in thickness. The middle Cerenkov element utilized a large photomultiplier (EMI 9522A) which significantly improved its particle discrimination capabilities. This arrangement allowed it to resolve upward and downward singly charged particles with an efficiency exceeding 98%. The detector performed crude pulse height analysis on the scintillator outputs, which provided an in-flight check of the detector's response. The B detector had a geometrical factor 9.8 ± 0.5 cm² sr.
The detector's efficiency varied depending on whether particles were absorbed in the upper lead block (L1) or penetrated to be absorbed in the lower block (L2). The device could separate electrons into low-energy (stopped in L1) and high-energy (penetrating to L2) components. The scintillators extended beyond the telescope's defined solid angle to minimize proton-nucleon scattering effects, covering a scattering angle of 20-25 degrees outside the most oblique direction defined by the telescope. The data from the detector was processed through flight electronics and transmitted via a 0.1 W FM transmitter operating at 137 MHz.
Details of the balloon flight
Balloon launched on: 10/13/1965 at
Launch site: Cardington, Bedfordshire, England
Balloon manufacturer/size/composition: Zero Pressure Balloon
End of flight (L for landing time, W for last contact, otherwise termination time): 10/13/1965
Balloon flight duration (F: time at float only, otherwise total flight time in d:days / h:hours or m:minutes - ): 9 h
External references
- Primary cosmic ray electrons below 600 MeV Planetary and Space Science, Volume 15, Issue 11, Pag. 1787 (1967)
If you consider this website interesting or useful, you can help me to keep it up and running with a small donation to cover the operational costs. Just the equivalent of the price of a cup of coffee helps a lot.