Purpose of the flight and payload description
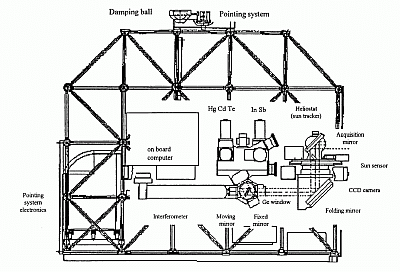
The LPMA instrument (Limb Profile Monitor of the Atmosphere) is a high spectral resolution Fourier transform spectrometer operating in absorption against the sun. The objective is to record limb atmospheric spectra in selected intervals from the thermal infrared to the near-infrared.
The instrument is composed by a commercial BOMEM DA2 spectrometer customized for balloon operations. A specially designed two detectors output optics enables to cover simultaneously two spectral regions making it possible to sample simultaneously the two interferograms detected during the same scan of the moving mirror and allowing to collect information on atmospheric species absorbing in widely different spectral regions.
In order to reach a good signal to noise ratio spectra performance, the interferometer must be feeded with a stable solar beam exactly aligned along the optical axis of the instrument. To be able to do this, two sub-systems of the gondola are needed:
- a primary pointing system initially developed by the Observatory of Geneva for astronomical payloads, controling the azimuth of the gondola and maintaining the sun in the field of view of the instrument even during ascent in the dense layers of the upper troposphere or lower stratosphere where this is a rather difficult achievement.
- a suntracker (also known as a heliostat) developed in cooperation with the Institut d'Electronique el de Micro-electronique du Nord performing the fine pointing of the acquisition mirror through 2 axes servo-controlled gimbal compensating for the residual motions of the payload and maintaining a jitter of the solar beam direction at the input of the interferometer of less than 1 arc min.
In addition it is possible to accomodate on the gondola another instrument of the class 30-50 kg wich can benefit from their good pointing capabilities.
Details of the balloon flight
Balloon launched on: 3/14/1992 at 14:23 utc
Launch site: European Space Range, Kiruna, Sweden
Balloon launched by: Centre National d'Etudes Spatiales (CNES)
Balloon manufacturer/size/composition: Zero Pressure Balloon
End of flight (L for landing time, W for last contact, otherwise termination time): 3/14/1992
Landing site: Free fall from 32 km on a frozen lake near Nikel, Russia. Instrument destroyed.
Campaign: EASOE (European Arctic Stratospheric Ozone Experiment) was undertaken in the northern winter of 1991-92 to study the processes in the Arctic which lead to ozone destruction and their connection with reduced ozone at northern mid-latitudes.
During or shortly after cut-down operation of the last flight, the shaft of the azimuth decoupling system broke, and the gondola came down in free-fall from 32 km altitude. Upon impact on a frozen lake near Nikel, Russia, the whole instrument was completely destroyed.
However 43 spectra were obtained during the flight between 11.5 km and 26.4 km during ascent, before the free fall of the payload. The interferograms were restored from the onboard recorder tape that was recovered from the wreck and processed at the 3M facility in Germany.
External references
- LPMA project website Laboratoire de Physique Moléculaire pour l'Atmosph&eagrave;re et l'Astrophysique (via Archive.Org)
- List of balloons launched from ESRANGE SSC Space website (via Archive.Org)
- Partial dataset of measurements obtained by LPMA during the flight Centre for Environmental Data Analysis (UK)
If you consider this website interesting or useful, you can help me to keep it up and running with a small donation to cover the operational costs. Just the equivalent of the price of a cup of coffee helps a lot.