Purpose of the flight and payload description
LEE (Low Energy Electron) was an instrument created to measure the energy spectrum of cosmic ray electrons. It was developed in the late 1960's decade at the University of Chicago. Regular balloon flights have been made from Northern Canada every year from 1968 to 1975 and approximately bi-annually until 1979. Then, the experiment was transfered to the University of Delaware, wich now operates it. The observations from LEE provided the scientific community with one of the more precise measurements of the electron spectrum over a period of time of more than 50 years.
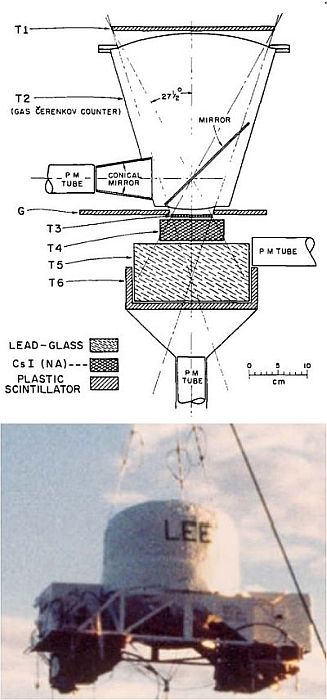
In the picture at left we can see a basic scheme of LEE and the instrument ready to flight on its gondola. The design remained intact since its inception with only minor upgrades made periodically. It consisted of a counter telescope made of NE 102 A plastic scintillators, a CsI(T1) scintillator, a gas Cerenkov counter, a lead glass Cerenkov counter, and a plastic penetration counter. Basically, the LEE instrument measured electron energies by causing incoming electrons to shower and recording the resulting signals from the shower counters. The maximum angle of acceptance was 27.5° from vertical, and the geometry factor was 18 cm2 sterad, defined by the two plastic scintillators T1 and T3. These two counters had diameters of 28 cm and 7 cm and thicknesses of 0.5 cm and 0.32 cm respectively. The gas Cerenkov counter T2 consisted of a conical container filled with Freon 12 at 2.5 atmospheres of pressure. The T1, T2, T3 coincidence was used to initiate the measuring process for each event.
Located under this telescope were a CsI counter (T4) of a thickness corresponding to 2 radiation lengths and a lead glass Cerenkov counter (T5), 6.7 radiation lengths thick. Particles entering the telescope were either absorbed or, together with their secondaries, penetrated the plastic cup counter T6. The reason for introducing two separate counters T4 and T5 was that this separation permited distinguishing electrons from interacting protons at high energies, and that counter T4 provided good energy resolution for electrons at low energies.
The output of counter T6 served as an additional parameter for energy determination in those cases where the energy of the initiating electron was sufficiently high that the shower penetrated T5. The output from T6 yielded the number of penetrating shower particles. The addition of a guard counter G, whose firing in coincidence with the master pulse T1 T2 T3 was indicated, served to identify events which were triggered by showers initltated above and around the apparatus. It also rejected events in which secondary particles entered the window of the gas counter photomultiplier leading to a false triggering of T2 by Cerenkov light produced in the window material. For each event, pulse heights were measured from counters T3, T4, T5 and T6 by 256 channel analyzers. The information on rates and pulse heights was digitized by the electronics system and recorded by an on-board magnetic tape recorder as well as telemetered to the ground.
The entire system was housed in an aluminum shell and kept under atmospheric pressure during the balloon flight. The weight of the instrument in its shell and including batteries amounted to approximately 400 lb.
Details of the balloon flight
Balloon launched on: 8/31/1979 at 5:30 utc
Launch site: Thompson, Manitoba, Canada
Balloon launched by: National Scientific Balloon Facility (NSBF)
Balloon manufacturer/size/composition: Zero Pressure Balloon Winzen 436.079 m3 (12.70 microns Stratofilm)
Flight identification number: 161N
End of flight (L for landing time, W for last contact, otherwise termination time): 9/1/1979
Balloon flight duration (F: time at float only, otherwise total flight time in d:days / h:hours or m:minutes - ): F 30 h 30 m
Payload weight: 634 kgs.
External references
- A detector system for cosmic ray electrons Nuclear Instruments and Methods, 85(1), Pag. 93, 1970
- National Scientific Balloon Facility Annual Report FY 1979 National Center for Atmospheric Research, September 1980
- Solar Modulation of' Cosmic Ray Electrons 1978-1983 J. Geophys. Res., 89(A5), 26472654, 1984
If you consider this website interesting or useful, you can help me to keep it up and running with a small donation to cover the operational costs. Just the equivalent of the price of a cup of coffee helps a lot.