Purpose of the flight and payload description
The objective of the flight was to obtain large air samples using a balloon-borne cryogenic sampler. The instrument was designed at the Max-Planck-Institut fur Chemie, in Mainz, Germany following the line of a similar instrument developed by the U.S. National Center of Atmospheric Research (NCAR) in early 1970's.
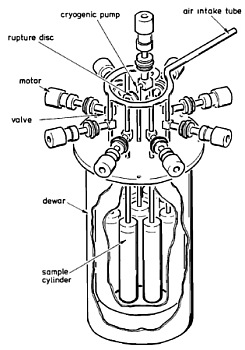
In the image at left can be seen a drawing of the sampler (click to enlarge). It was composed by eight evacuated sampling tubes of 300-ml volume made of stainless steel which were immersed in liquified neon. The neon was kept under a constant pressure of 1.5 bar at a temperature of 28.6 degrees Kelvin. Through motor-driven valves activated by telecommand, the tubes were connected to a manifold and an air intake. When a valve was opened, the outside air was immediately sucked in and sublimated on the cold walls of the sampling tube. Hence the opening time determined the quantity of air sampled at a given ambient pressure. A ninth tube was used as a pump to flush the manifold and air intake tube prior to each sampling. To eliminate or at least minimize the effect of outgassing and wall reactions (interior contamination), all interior surfaces of the sampler were electropolished. The complete system of air intake tube, manifold, and sampling tubes was baked out at 380º C for 2 weeks, 1 week under high vacuum and then 1 week with the system filled with synthetic air.
During each flight, several samples were obtained at different altitudes up to a capacity of about 10 liters of air (at standard temperature and pressure). The collecting procedure required about 20 min at an altitude of 35 km (due to the low atmospheric pressure) while the time at a lower altitude of 15 km (and increased ambient pressure) was about 1 minute. Exterior contamination from the balloon system was eliminated during the flights by taking air samples only during the slow descent of balloon, at a rate of about 50-100 m/min. This was achieved by releasing gas through a remotely controlled valve on top of the balloon. The distance between the balloon and the sampler was about 200 meters. For reasons of undisturbed data transmission the CNES telemetry/telecommand unit had to be suspended immediately below the gondola. As it was thermally insulated with polystyrene, the device was sealed in a polyethylene bag so that outgassing freons from it, did not affect the samples.
Extreme care was taken to avoid contamination from the cryosampler itself by sealing it in a vacuum-proof stainless steel container. The neon refrigerant was vented through a pressure valve and a black tank that absorbed sufficient solar energy to heat it to at least ambient temperatures. Two beams, 6 meters length each, were attached to the gondola, one for the neon exhaust and one on the opposite side for the sample intake. Such an arrangement prevented the exhausted neon from being collected with the samples.
Details of the balloon flight
Balloon launched on: 9/26/1977 at
Launch site: Centre de Lancement de Ballons CLBA, Aire Sur L'Adour, Landes, France
Balloon launched by: Centre National d'Etudes Spatiales (CNES)
Balloon manufacturer/size/composition: Zero Pressure Balloon model 100z Zodiac - 100.000 m3
End of flight (L for landing time, W for last contact, otherwise termination time): 9/26/1977
External references
- Atmospheric sampling Advances in Space Research, Volume 1, Issue 11, 1981, Pag. 17
- Simultaneously measured vertical profiles of H2, CH4, CO, N2O, CFCl3, and CF2Cl2 in the mid-latitude stratosphere and troposphere J. Geophys. Res., 84(C6), 31493154
- The vertical distribution of stable trace gases at mid-latitudes J. Geophys. Res., 86( C6), 5179 (1981)
If you consider this website interesting or useful, you can help me to keep it up and running with a small donation to cover the operational costs. Just the equivalent of the price of a cup of coffee helps a lot.