Purpose of the flight and payload description
The objective of the mission was to measure the spectra of the specific ionization of the primary cosmic radiation, as part of a series of balloon-flights over Germany performed between April 1957 and August 1960.
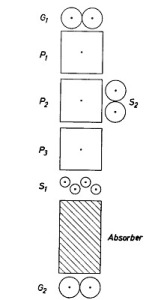
The payload was composed mainly by a counter telescope, whose arrangement is shown in the figure at left.
Three proportional counters P1, P2, P3 were used to measure the specific ionization of each allowed particle. The smallest of these ionization losses was selected automatically to reduce the fluctuations due to large energy transfer. Two trays of Geiger counters G1, G2 defined the solid angle, the groups of Geiger counters, S1 and S2 performed an elimination of shower events originated internally or externally.
An absorber was used to exclude slow particles to ensure the necessary resolution in the charge spectrum. The total absorber consisted of 82.8 g/cm2 copper (setting an instrumental cut-off energy for protons of 320 MeV). To reach the lowest proportional counter a particle had to penetrate a layer of 5.8 g/cm2.
For this particular flight a separate telescope of Geiger counters was added to measure the intensity of low energy particles.
Details of the balloon flight
Balloon launched on: 8/23/1960 at 5:55 local
Launch site: Lindau, West Germany
Balloon launched by: Max-Planck Institut fur Aeronomie
Balloon manufacturer/size/composition: Zero Pressure Balloon 3.820 m3
End of flight (L for landing time, W for last contact, otherwise termination time): ??/??/1960
Overall weight: 54 kg
External references
- Alpha particle and proton fluxes of the primary cosmic radiation and their time variations Journal of Atmospheric and Terrestrial Physics, Volume 24, Issue 9, September 1962, P. 779
- Schwankungen der primären kosmischen Strahlung Zeitschrift für Naturforschung A, Volume 17, Issue 2, pp.135
If you consider this website interesting or useful, you can help me to keep it up and running with a small donation to cover the operational costs. Just the equivalent of the price of a cup of coffee helps a lot.